STEP ONE
Choose a possible topic route
Choosing a topic route is about getting from a broad subject area that interests you down to one or two possible sub-fields that could form a large proportion of the replication-based dissertation that you take on. In the diagram below, we have highlighted the three steps you need to follow to achieve this, using the degree of Management as our example.
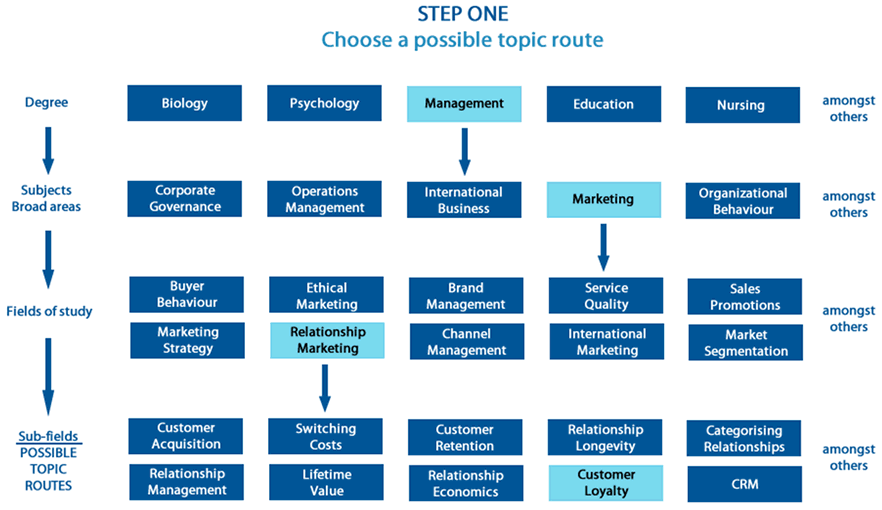
Now, thinking about your own degree, work through the following three steps for yourself: (STEP A) Choose the broad subject area that interests you most; (STEP B) Identify the fields within this broad subject area, and select one (or more) fields that interest you most; and (STEP C) Identify the sub-fields within these fields, and select one (or more) sub-fields that interest you most. Each of these steps is discussed in turn:
STEP A
Choose the broad subject area that interests you most
Within your degree, you will have covered a wide range of subjects (e.g., within the degree of Management, such subjects include Corporate Governance, Operations Management, International Business, Marketing, Organizational Behaviour, etc.). A single journal article can cover more than one of these broad subject areas at once, but a lot will draw from the fields and sub-fields within just one (or sometimes two) of these broad subject areas. Whilst we talk about these fields next, start by choosing one of these broad subject areas that you found most interesting and/or easy to understand during your studies. When taking on a Route #1: Replication-based dissertation at the undergraduate or master's dissertation level, we would recommend choosing just one of these broad subject areas because the more you take on, the wider the literature review that you will have to perform later on. If you're a doctoral student, this is one thing, but you're unlikely to have time to do this properly at the undergraduate or master's level, which can often result in the criticism that your dissertation topic is too broad and is insufficiently critical. Avoid this by choosing just one broad subject area (e.g., we chose the subject area, Marketing, within the degree of Management).
STEP B
Identify the fields within this broad subject area, and select one (or more) fields that interest you most
Again, ask yourself questions: What am I most interested in? What do I find easiest to understand? However, this time, focus in on the fields of study (i.e., narrower areas) within the broad subject areas you chose in STEP A above. For example, within the broad subject area of Marketing, there are many fields, such as Buyer Behaviour, Ethical Marketing, Brand Management, Marketing Strategy, and so on, but in our example, we chose Relationship Marketing. Again, whilst you could choose more than one of these fields, we recommend keeping it simple and manageable at this stage, keeping to a maximum of two fields.
STEP C
Identify the sub-fields within these fields, and select one (or more) sub-fields that interest you most
When you take this one step further, looking at the sub-fields within your chosen fields, a number of possible topic routes start to emerge (e.g., within the field of Relationship Marketing, there are a wide range of sub-fields, such as Customer Acquisition, Switching Costs, Customer Retention, Relationship Longevity, etc.). In our example, we chose to focus in on Customer Loyalty. At this stage, would recommend adopting one of two approaches:
Approach #1: choose a single sub-field, and then explore the possible main journal articles that emerge from this single sub-field.
Approach #2: choose a number of sub-fields, narrowing down the list of possible main journal articles that will emerge.
If you are particularly keen on a single sub-field or want more options to consider, we would recommend choosing Approach #1 because when you generate a list of potential journal articles in STEP TWO, which follows, searching using a single sub-field will give you a list of potential journal articles that include the sub-field you are particularly interested in, but also give you a much wider range of other sub-fields that might interest you. Approach #2 will substantially narrow down the options in your list (i.e., the number of possible journal articles), which is usually only useful if you are only keen on exploring a specific topic area (e.g., research in journal articles that only looked at Customer Loyalty, Switching Costs and Relationship Longevity at the same time). When you have chosen the sub-field(s) that interest you most, move onto STEP TWO.